
3 The hepatoprotective nature of silymarin includes enhanced detoxification, anti-lipid peroxidation and antioxidation. Silymarin also protects the liver cells from ischemic injury, radiation, iron toxicity and viral hepatitis. Silymarin, milk thistle extract (Silybum marianum) has been a natural remedy for liver related disorders and hepatic protection from various toxins. The liquid lipid in the core aids the spherical morphology of the particles. This lipidic blend exhibits a slower polymeric transition and a low crystallinity index. Thus, more amount of drug dissolves in the liquid lipid and simultaneous encapsulation in the solid lipid.
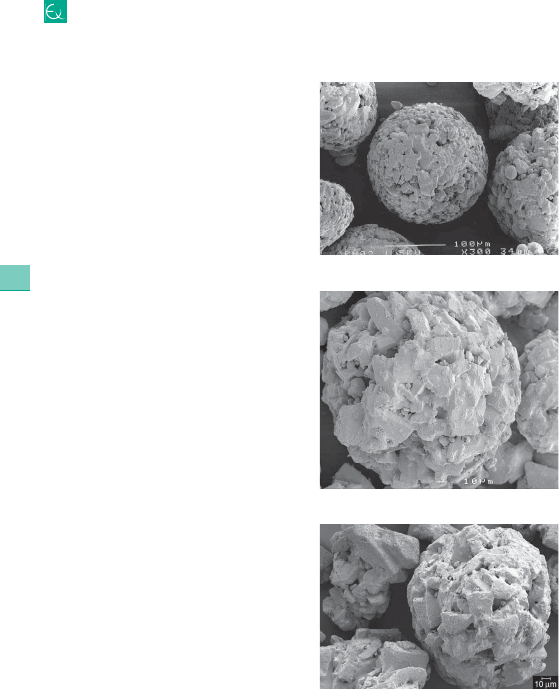
1 The NLCs produce particles where liquid lipid is blended with the solid lipid core. The NLCs contain partially crystallized and less ordered crystalline structure lipid droplets. SLNs are modified into NLCs by combining solid lipid (fat) with liquid lipid (oil). Important lipid based systems include nano- and microemulsions, liposomes, solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs), and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs). The lipid system facilitates bioactive molecule absorption in the small intestine because of the formation of micelles that solubilize and transport lipophilic molecules. As most bioactive molecules are lipophilic, colloidal dispersions are often required in aqueous environments. Commercial use of polymer systems is restricted due to their toxicity, lack of suitable production scale, minimal number of biopolymers and use of organic solvents. Nanotechnology based formulations have important prospects in pharmaceutics and can generally be divided into two groups: polymer- and lipid-based systems. The solid dry powder is used for oral reconstitution and can be further converted into tablets or filled into capsules. Dispersion stability was increased by preparing the DANs. The ex-vivo permeation study for optimized NLC formulation exhibited the lymphatic uptake of active. Ex-vivo permeation in the presence and absence of lymphatic blocker indicates the uptake of silymarin loaded NLCs by the lymphatic route.Ĭonclusions: Silymarin loaded NLCs prepared had a nanosize distribution with high entrapment efficiency. In-vitro release studies showed sustained drug release for up to 24 h. The particles were spherical with smooth surface morphology.


The X-ray diffraction and endothermic peaks confirmed the maximum encapsulation of active in lipid matrices. Results: The optimized NLCs have a mean particle size of 206.1☐12.5 nm (size distribution of 0.249☐.058), a zeta potential of -32.5☑.2 mV with high entrapment of 95.60☐.45% and drug loading of 1.90☐.08%. NLCs and DANs were characterized for particle size, polydispersity index, zeta potential, entrapment efficiency, drug loading, assay, thermal behavior, crystallinity and morphological study. For better stability, NLC dispersion was converted into DANs by adsorbing them onto some suitable carriers. Methods and Material: Silymarin loaded NLCs were prepared by a modified hot melt emulsification ultra-sonication method using glyceryl monostearate (GMS), capmul MCM C8 EP (CAP) and gelucire 50/13 (G50/13) as solid lipid, liquid lipid and surfactant respectively. The prepared silymarin loaded NLCs and DANs were characterized for various quality parameters. Aims: The present study was aimed at preparing stable dry adsorbed nanoparticles (DANs) of silymarin loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
